Chart"
m (correct highlight (via JWB)) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | Components: < | + | Components: <code>chart</code> |
A chart is used to show a set of data as a graph, which helps users to digest data quickly. | A chart is used to show a set of data as a graph, which helps users to digest data quickly. | ||
| − | In order to use a < | + | In order to use a <code>chart</code> component we only need to prepare a suitable data model and give it to the chart. The following is an example of pie chart. |
[[Image:10000000000001370000005ED5356D68.png]] | [[Image:10000000000001370000005ED5356D68.png]] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=== Live Data === | === Live Data === | ||
| − | The above example is a little misleading. In fact, developers don't have to prepare real data before feeding it into a < | + | The above example is a little misleading. In fact, developers don't have to prepare real data before feeding it into a <code>chart</code> as <code>chart</code> components support live data mechanism. With live data, developers are able to separate the data from the view enabling the developer to add, update and remove data from the data model with the framework taking care of redrawing the <code>chart</code>. For advanced implementations, developers can even provide their own chart model by implementing the <javadoc type="interface">org.zkoss.zul.ChartModel</javadoc> interface. |
=== Drill Down (The onClick Event) === | === Drill Down (The onClick Event) === | ||
| − | Sometimes a user wants more details on a section of a chart, such as a piece of the pie chart or a bar of the bar chart. This functionality is provided as each part of the of the < | + | Sometimes a user wants more details on a section of a chart, such as a piece of the pie chart or a bar of the bar chart. This functionality is provided as each part of the of the <code>chart</code> is split up into <code>area</code> components allowing the users to click on them. When clicked they will fire an <code>onClick</code> event. Developers can then extrapolate the information from the <code>area</code> component and display it. |
| − | Each < | + | Each <code>area</code> component’s <code>componentScope</code> contains information that developers can use. |
{| border="1px" | {| border="1px" | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | In the following example, we provide an < | + | In the following example, we provide an <code>onClick</code> event listener for the <code>chart. </code>It locates the associated <code>area</code> component and shows the <code>area</code> category. |
<source lang="xml" > | <source lang="xml" > | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
=== Manipulate Areas === | === Manipulate Areas === | ||
| − | Chart components also provide an area renderer meaning developers can manipulate the attributes of a < | + | Chart components also provide an area renderer meaning developers can manipulate the attributes of a <code>chart’s</code> <code>area</code> components. |
There are only two steps needed to use the area renderer. | There are only two steps needed to use the area renderer. | ||
| − | # Implement the <javadoc type="interface">org.zkoss.zul.event.ChartAreaListener</javadoc> interface for manipulating area components. e.g. Change the < | + | # Implement the <javadoc type="interface">org.zkoss.zul.event.ChartAreaListener</javadoc> interface for manipulating area components. e.g. Change the <code>tooltiptext</code> of the <code>area</code>. |
| − | # Set the listener object or listener class name to the < | + | # Set the listener object or listener class name to the <code>chart</code>'s <code>areaListener</code> attribute. |
| − | Using this method, developers have a change to change the area component’s attributes and insert more information in the < | + | Using this method, developers have a change to change the area component’s attributes and insert more information in the <code>componentScope</code> for use within the application. |
{{ ZKDevelopersGuidePageFooter}} | {{ ZKDevelopersGuidePageFooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:41, 19 January 2022
![]() This documentation is for an older version of ZK. For the latest one, please click here.
This documentation is for an older version of ZK. For the latest one, please click here.
Components: chart
A chart is used to show a set of data as a graph, which helps users to digest data quickly.
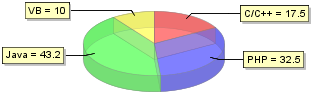
In order to use a chart component we only need to prepare a suitable data model and give it to the chart. The following is an example of pie chart.
<zk>
<chart id="mychart" type="pie" width="400" height="200" threeD="true" fgAlpha="128">
<zscript><![CDATA[
PieModel model = new SimplePieModel();
model.setValue("C/C++", new Double(17.5));
model.setValue("PHP", new Double(32.5));
model.setValue("Java", new Double(43.2));
model.setValue("VB", new Double(10.0));
mychart.setModel(model);
]]>
</zscript>
</chart>
</zk>
Different types of chart are used to demonstrate different kind of data thus, a chart needs to be provided a suitable data model. To use a pie chart, developers must provide use a PieModel as their data model while bar chart, line chart, area chart, and waterfall chart needs CategoryModel and XYModel.
Live Data
The above example is a little misleading. In fact, developers don't have to prepare real data before feeding it into a chart as chart components support live data mechanism. With live data, developers are able to separate the data from the view enabling the developer to add, update and remove data from the data model with the framework taking care of redrawing the chart. For advanced implementations, developers can even provide their own chart model by implementing the ChartModel interface.
Drill Down (The onClick Event)
Sometimes a user wants more details on a section of a chart, such as a piece of the pie chart or a bar of the bar chart. This functionality is provided as each part of the of the chart is split up into area components allowing the users to click on them. When clicked they will fire an onClick event. Developers can then extrapolate the information from the area component and display it.
Each area component’s componentScope contains information that developers can use.
| entity | Entity type of the area. (e.g. TITLE, DATA, CATEGORY, LEGEND) |
| series | Series name of the associated data (CategoryModel, XYModel, or HiLoModel). |
| category | Category name of the associated data (PieModel or CategoryModel). |
| URL | A string URL which can be used to drill down to a legacy page. |
| value | Numeric value of the associated data ( PieModel or CategoryModel). |
| x | The x value of the associated data (XYModel). |
| y | The y value of the associated data (XYModel). |
| date | The date value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
| open | The open value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
| high | The high value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
| low | The ow value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
| close | The close value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
| volume | The volume value of the associated data (HiLoModel). |
In the following example, we provide an onClick event listener for the chart. It locates the associated area component and shows the area category.
<zk>
<chart id="mychart" type="pie" width="400" height="250">
<attribute name="onClick">
alert(self.getFellow(event.getArea()).getAttribute("category"));
</attribute>
<zscript><![CDATA[
PieModel model = new SimplePieModel();
model.setValue("C/C++", new Double(17.5));
model.setValue("PHP", new Double(32.5));
model.setValue("Java", new Double(43.2));
model.setValue("VB", new Double(10.0));
mychart.setModel(model);
]]>
</zscript>
</chart>
</zk>
Manipulate Areas
Chart components also provide an area renderer meaning developers can manipulate the attributes of a chart’s area components.
There are only two steps needed to use the area renderer.
- Implement the ChartAreaListener interface for manipulating area components. e.g. Change the
tooltiptextof thearea. - Set the listener object or listener class name to the
chart'sareaListenerattribute.
Using this method, developers have a change to change the area component’s attributes and insert more information in the componentScope for use within the application.