Difference between revisions of "Template:Tutorial Approach Comparison"
(Created page with "= Approach Comparison = <!-- list strength for users --> Here is the architecture picture to demonstrate the interaction between Model, View, and Controller/ViewModel. [[Image...") |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Here is the architecture picture to demonstrate the interaction between Model, View, and Controller/ViewModel. | Here is the architecture picture to demonstrate the interaction between Model, View, and Controller/ViewModel. | ||
| − | [[Image:tutorial-mvc.png | + | [[Image:tutorial-mvc.png ]][[File:tutorial-mvvm.png]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The main differences are that '''Controller''' changes to '''ViewModel''' and there is a binder in MVVM to synchronize data instead of a Controller. | The main differences are that '''Controller''' changes to '''ViewModel''' and there is a binder in MVVM to synchronize data instead of a Controller. | ||
Revision as of 03:16, 21 June 2021
Approach Comparison
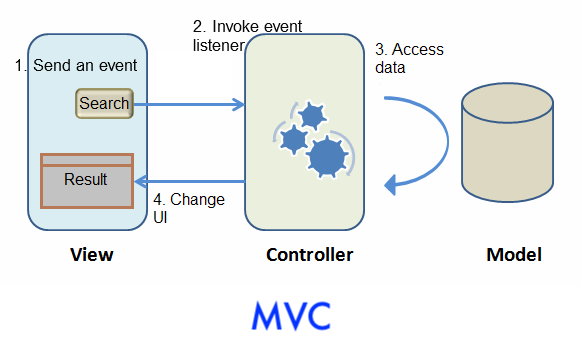
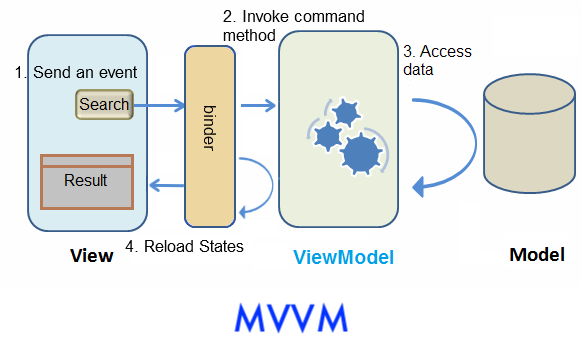
Here is the architecture picture to demonstrate the interaction between Model, View, and Controller/ViewModel.
The main differences are that Controller changes to ViewModel and there is a binder in MVVM to synchronize data instead of a Controller.
Briefly speaking, MVC advantage:
- very intuitive, easy to understand
- control components in fine-grained
MVVM advantage:
- suitable for design-by-contract programming
- loose coupling with View
- better reusability
- better testability
- better for responsive design
Both approaches can achieve many things in common, but there are still some differences between them. Each of two approaches has its strength. Building an application with MVC approach is more intuitive because you directly control what you see. Its strength is that you have total control of components so that you can create child components dynamically, control custom components, or do anything a component can do.
In MVVM, because ViewModel is loosely-coupled with View (it has no reference to components), one ViewModel may associate with multiple Views without modification. UI designers and programmers may work in parallel. If data and behavior do not change, a View's change doesn't cause ViewModel to be modified. In addition, as ViewModel is a POJO, it is easy to perform unit test on it without any special environment. That means ViewModel has better reusability, testability, and better resistance to View change.
To summarize, a comparison table is illustrated below:
| Coupling with View | Loose with layout | Loose |
|---|---|---|
| Coupling with Component | Tight | Loose |
| Coding in View | Component ID | Data binding expression |
| Controller Implementation | Extends ZK's composer | a POJO |
| UI Data Access | Direct access | Automatic |
| Backend Data Access | Direct access | Direct access |
| UI Updating | Manipulate components | Automatic(@NotifyChange) |
| Component Controlling Granularity | Fine-grained | Normal |
| Performance | High | Normal |