Window"
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<source lang="xml" > | <source lang="xml" > | ||
| − | + | <window title="Embedded Style" border="normal" width="200px">Hello, | |
| − | + | Embedded! | |
| − | Embedded! </window> | + | </window> |
| − | <window title="Overlapped Style" | + | <window title="Overlapped Style" mode="overlapped" border="normal" |
| − | + | width="200px">Hello, Overlapped! | |
| − | <window title="Popup Style" | + | </window> |
| − | + | <window title="Popup Style" mode="popup" border="normal" | |
| + | width="200px">Hello, Popup! | ||
| + | </window> | ||
| − | <window title="Modal Style" | + | <window title="Modal Style" mode="modal" border="normal" |
| − | + | width="200px">Hello, Modal! | |
| − | <window title="Highlight Style" | + | </window> |
| − | + | <window title="Highlight Style" mode="highlighted" border="normal" | |
| − | + | width="200px">Hello, Highlighted! | |
| + | </window> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Revision as of 06:46, 3 January 2020
Window
Employement/Purpose
A window is, like HTML DIV tag, used to group components. Unlike other components, a window has the following characteristics.
- A window is an owner of [[an ID space. Any component contained in a window, including itself, could be found by use of Component.getFellow(String), if it is assigned with an identifier.
- A window could be overlapped, popup, and embedded.
- A window could be a modal dialog.
Example
<window title="Embedded Style" border="normal" width="200px">Hello,
Embedded!
</window>
<window title="Overlapped Style" mode="overlapped" border="normal"
width="200px">Hello, Overlapped!
</window>
<window title="Popup Style" mode="popup" border="normal"
width="200px">Hello, Popup!
</window>
<window title="Modal Style" mode="modal" border="normal"
width="200px">Hello, Modal!
</window>
<window title="Highlight Style" mode="highlighted" border="normal"
width="200px">Hello, Highlighted!
</window>
Window Modes
A window could be in one of five different modes:
- embedded (default)
- overlapped
- popup
- modal
- highlighted and
You could change the mode by the use of Window.setMode(String).
<window title="Hi, I'm Overlapped" border="normal" mode="overlapped">
...
</window>
Alternatively, you could invoke one of Window.doOverlapped(), Window.doPopup(), Window.doModal(), Window.doHighlighted(), and Window.doEmbedded(), as shown below.
<zk>
<window id="win" title="Hi!" border="normal" width="200px">
<caption>
<toolbarbutton label="Help"/>
</caption>
<checkbox label="Hello, Wolrd!"/>
</window>
<button label="Overlap" onClick="win.doOverlapped();"/>
<button label="Popup" onClick="win.doPopup();"/>
<button label="Modal" onClick="win.doModal();"/>
<button label="Embed" onClick="win.doEmbedded();"/>
<button label="Highlighted" onClick="win.doHighlighted();"/>
</zk>
Embedded
An embedded window is placed inline with other components. In this mode, you cannot change its position, since the position is decided by the browser. It is the default mode since it is the most common appearance.
Overlapped
An overlapped window is overlapped with other components, such that users could drag it around and developer could set its position by Window.setLeft(String) and Window.setTop(String).
<window title="My Overlapped" width="300px" mode="overlapped">
</window>
An overlapped window is typically used to display the information that should co-exist with the current operation and should appear for a long time. You might have multiple overlapped windows and each for different set of information. If you want to show the information that will appear only temporarily (dismissed as soon as a user clicks somewhere else), you could use the popup mode as described in the next section, or the Popup component.
Popup
A popup window is similar to overlapped windows, except it is automatically closed when user clicks on any component other than the popup window itself or any of its descendants. Of course, you could dismiss it manually by making it invisible or detaching it.
As its name suggested, it is designed to implement the popup windows. A typical application is to display information that won't obscure the current operation and are easy to close. A popup window is usually position around the focal point (such as a button). It can be done by use of Window.setPosition(String) with parent.
For example, we could display a popup window right after a button as depicted below.
<zk>
<toolbarbutton label="More info" onClick="info.doPopup()"/><span>
<window id="info" visible="false" width="120px" border="normal" position="parent">
Here is more information
</window>
</span>
</zk>
where we specify position="parent", and make it as a child of a span component. The span component acts as an anchor point and the window is posited based on it.
In additions to popup windows, you could use Popup for displaying a popup. The popup component has more control how to position it (by the use of Popup.open(Component, String)).
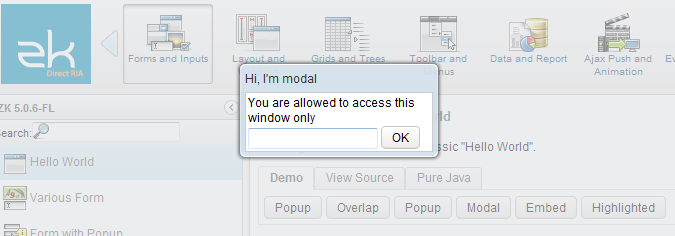
Modal and Highlighted
By default, a modal window is the same as a highlighted window. Unless you configure ZK to enable the event thread (see the next section), you could consider them as exactly same.
A modal window provides the so-called modal effect that limits a user from accessing components other than the modal window. Users cannot access anything outside of the modal window, including clicking or tabbing.
For instance, you could access only the textbox and button in the following example:
To dismiss a modal window, you could make it invisible (Window.setVisible(boolean)), or detach it from a page.
By default, a modal window is positioned at the center of the browser window. You could change the position by Window.setPosition(String).
You could have multiple modal windows at the same time, and the user could only access the last modal window. Once the last modal is dismissed (invisible or detached), the previous modal window will become the active modal window until it is dismissed.
Modal Windows and Event Processing Threads
By default[1], events are processed in the same thread that serves the HTTP request (so-called Servlet thread). However, you could configure ZK to process events in an individual thread, such that the event listener could suspend the execution at any time, and resume later. For how to enable the event processing thread, please refer to ZK Configuration Reference.
Notice that, for better integration with other frameworks, such as Spring, it is suggested to disable the event processing thread (default). For more information, please refer to the Event Threads section.
Once the event thread is enabled, a modal window will behave differently from other modes: Window.doModal() will suspend the execution until dismissed (invisible, detached or mode changed). It is convenient to implement something that has to wait for user's further input.
As depicted in the following example, f1() is called only after win1 is dismissed, while g1() is called immediately right after win2 becomes highlighted:
win1.doModal(); //the execution is suspended until win1 is closed
f1();
win2.doHighlighted(); //the execution won't be suspended
g1()
- ↑ Event processing thread is disabled by default since 5.0. For older version, it is enabled by default.
Properties and Features
Border
The border property (Window.setBorder(String)) specifies whether to display a border for window. The default style sheets support only normal and none. The default value is none, i.e., no border.
Closable
By setting the closable property (Window.setClosable(boolean)) to true, a close button is shown for the window, which enables a to close the window by clicking the button. Once the user clicks on the close button, an onClose event is sent to the window which is processed by the onClose method of the Window component. Then, onClose, by default, detaches the window itself.
The onClose Event
You can override it to do whatever you want. Or, you can register your own listener to change the default behavior. For example, you might choose to hide the window rather than close it.
<window closable="true" title="Detach on Close" border="normal" width="200px"
onClose="self.visible = false; event.stopPropagation();">
In this example, this window hides itself when the close button is clicked.
</window>
</zk>
Notice that event.stopPropagation() (Event.stopPropagation()) must be called to prevent the default onClose handler (Window.onClose()) being called.
Tip: If the window is a popup, the onOpen event will be sent to the window with open=false, when the popup is closed due to the user clicking outside of the window, or pressing ESC.
The onClose is sent to ask the server to detach or to hide the window. By default, the window is detached. Of course, the application can override this behaviour and do whatever it wants as described above.
On the other hand, onOpen is a notification. It is sent to notify the application that the client has hidden the window. The application cannot prevent it from hiding, or changing the behavior to be detached.
ContentStyle and ContentSclass
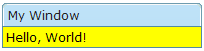
You can customize the look and feel of window's content block by specifying the contentStyle property (Window.setContentStyle(String)).
<zk>
<window title="My Window" border="normal" width="200px" contentStyle="background:yellow">
Hello, World!
</window>
</zk>
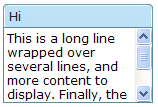
Scrollable Window
A typical use of the contentStyle attribute is to make a window scrollable as follows.
<window id="win" title="Hi" width="150px" height="100px" contentStyle="overflow:auto" border="normal">
This is a long line wrapped over several lines, and more content to display.
Finally, the scrollbar becomes visible.
This is another line.
</window>
Note: For IE 7's overflow bug, also use position:relative with overflow:auto
Position
In addition to the left and top properties, you can control the position of an overlapped/popup/modal/highlighted window by the use of the position attribute. For example, the following code snippet positions the window to the right-bottom corner.
<window width="300px" mode="overlapped" position="right,bottom">
...
The value of the position attribute can be a combination of the following constants by separating them with comma (,).
| Position the window at the center. If left or right is also specified, it means the vertical center. If top or bottom is also specified, it means the horizontal center. If none of left, right, top and bottom is specified, it means the center in both directions.
Both the left and top property are ignored. | |
| Position the window at the left edge.
The left property is ignored. | |
| Position the window at the right edge.
The left property is ignored. | |
| Position the window at the top.
The top property is ignored. | |
| Position the window at the bottom.
The top property is ignored. |
By default, its value is null. That is, the overlapped and popup window is positioned by the left and top properties, while the modal window is positioned at the center.
Sizable
If you allow users to resize the window, you can set the sizable attribute to true as follows.
<window id="win" title="Sizable Window" border="normal" width="200px" sizable="true">
This is a sizable window.
<button label="Change Sizable" onClick="win.sizable = !win.sizable"/>
</window>
Once allowed, users can resize the window by dragging the borders.
The onSize Event
Once a user resizes the window, the onSize event is sent with an instance of the org.zkoss.zul.event.SizeEvent. Notice that the window is resized before the onSize event is sent. In other words, the event serves as a notification that you generally ignore. Of course, you can do whatever you want in the event listener.
Note: If the user drags the upper or left border, the onMove event is also sent since the position has changed, too.
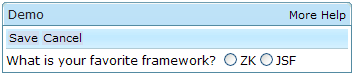
Title and Caption
A window might have a title, a caption and a border. The title is specified by the title attribute. The caption is specified by declaring a child component called caption. All children of the caption component will appear on right hand side of the title.
<zk>
<window title="Demo" border="normal" width="350px">
<caption>
<toolbarbutton label="More" />
<toolbarbutton label="Help" />
</caption>
<toolbar>
<toolbarbutton label="Save" />
<toolbarbutton label="Cancel" />
</toolbar>
What is your favorite framework?
<radiogroup>
<radio label="ZK" />
<radio label="JSF" />
</radiogroup>
</window>
</zk>
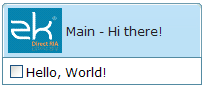
You are also able to specify a label and an image within a caption, and then the appearance is as follows.
<zk>
<window id="win" title="Main" border="normal" width="200px">
<caption image="/images/ZK-Logo.PNG" label="Hi there!"/>
<checkbox label="Hello, World!"/>
</window>
</zk>
Trouble shooting with browser issue
- There's a issue for Listbox/Grid in window , please reference
Grid in window get wrong display in IE7/IE6
Common Dialogs
The XUL component set supports the following common dialogs to simplify some common tasks.
Supported Events
| Event: Event
Denotes the position of the window is moved by a user. | |
| Event: OpenEvent
Denotes user has opened or closed a component. Note: Unlike onClose, this event is only a notification. The client sends this event after opening or closing the component. It is useful to implement load-on-demand by listening to the onOpen event, and creating components when the first time the component is opened. | |
| Event: Event
Denotes the close button is pressed by a user, and the component shall detach itself. | |
| Event: MaximizeEvent
Denotes user has maximize a component. | |
| Event: MinimizeEvent
Denotes user has minimize a component. | |
| Event: SizeEvent
Denotes the panel's size is updated by a user. | |
| Event: ZIndexEvent
Denotes the panel's zindex is updated by a user. |
- Inherited Supported Events: XulElement
Supported Children
*ALL
Use Cases
| Version | Description | Example Location |
|---|---|---|
| 5.0+ | How to create a modal Window and communicate with it | http://www.zkoss.org/forum/listComment/9785 |
| 3.6+ | Best practises on creating a pop-up window to display PDF reports | http://www.zkoss.org/forum/listComment/9305 |
Version History
| Version | Date | Content |
|---|---|---|