Box"
From Documentation
(→Box) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
= Box = | = Box = | ||
| − | |||
*Java API: <javadoc>org.zkoss.zul.Box</javadoc> | *Java API: <javadoc>org.zkoss.zul.Box</javadoc> | ||
*JavaScript API: <javadoc directory="jsdoc">zul.box.Box</javadoc> | *JavaScript API: <javadoc directory="jsdoc">zul.box.Box</javadoc> | ||
Revision as of 06:35, 21 April 2010
Box
Employment/Purpose
The box model of XUL is used to divide a portion of the display into a series of boxes. Components inside of a box will orient themselves horizontally or vertically. By combining a series of boxes and separators, you can control the layout of the visual presentation.
A box can lay out its children in one of two orientations, either horizontally or vertically. A horizontal box lines up its components horizontally and a vertical box orients its components vertically. You can think of a box as one row or one column from an HTML table.
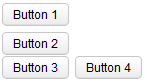
Example
<zk>
<box orient="vertical">
<button label="Button 1"/>
<button label="Button 2"/>
</box>
<box orient="horizontal">
<button label="Button 3"/>
<button label="Button 4"/>
</box>
</zk>
Supported events
| None | None |
Supported Children
*ALL
Use cases
| Version | Description | Example Location |
|---|---|---|
Version History
| Version | Date | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 5.0.1 | 4/21/2010 | Initialization |