DB Form Builder Inside Out"
m (Created page with '{{Template:Smalltalk_Author| |author=Charles Pao, Engineer, Potix Corporation |date=Mar 31, 2009 |version= }} #ZK version 3.6.0 and above #ZK Studio version 0.9.3 __TOC__ == …') |
|
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 07:38, 20 September 2010
Charles Pao, Engineer, Potix Corporation
Mar 31, 2009
- ZK version 3.6.0 and above
- ZK Studio version 0.9.3
Introduction
ZK Studio 0.9.3 brings a powerful Form Builder, called DB Form Builder. In this article, I'll show you how the DB Form Builder can let you build a DB Form, and how to customize it.
What is DB Form Builder
DB Form Builder is a Wizard to help developers to generate a DB Form[1] in seconds without typing any code.
Begin your first project with DB Form Builder
You can get acquaintance with DB Form Builder and learn how to make a DB Form in Step by Step Guide.
What was generated in your project
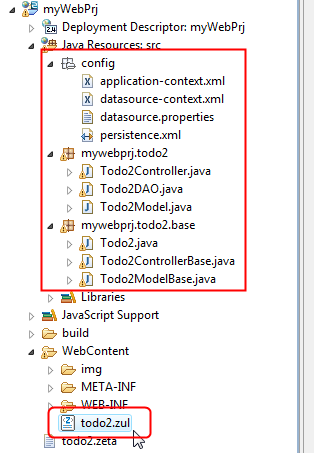
After you apply a DB Form Builder for a dynamic web project with ZK installed, you will notice the following files have been added to your web project:
(1) two packages with six generated Java files.
(2) one package called "config", which has four configuration files inside.
(3) several library jar files and their license information are copied into the /WebContent/WEB-INF/lib. (not shown in this snapshot)
(4) a zul file as the presentation means.
Let me explain what are those things for in the following sections.
Generated Java files and zul file
Those files are the main logic where the DB Form works, in short, it combines ZK with Spring framework, use JPA (with Hibernate implementation) to link to Database, and the ZK is the control and presentation layer.
You can take a look at ZK With Spring JPA And A Model-View-Controller Pattern to know the underlying mechanism of how ZK + Spring + JPA works.
I will use CodeName as the name typed in the last page of DB Form Builder afterwards.
First, the three .java files in "ProjectName.CodeName" packages are:
- The CodeNameController.java is the "Controller" in DB Form.
- The CodeNameDAO.java is a data access object (DAO) class used in DB Form.
- The CodeNameModel.java is the "Model" in DB Form.
And there is a generated zul file in the WebContent folder:
- The CodeName.zul is the "View" in DB Form.
We can do customization for these files, I'll show how to do it in Customize DB Form section.
Note:
The three files in "CodeName.base" package are the base classes of the MVC model of DB Form, they will be always replaced if you re-generate it again, please don't modify those files.
Configuration Files
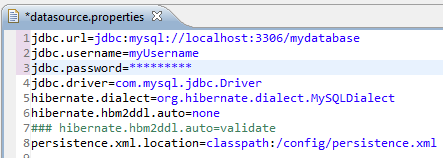
The four configuration files will be putted in the config package, and you only need to care application-context.xml and datasource.properties :
| application-context.xml | Spring framework configuration file |
| datasource-context.xml | JPA configuration file |
| datasource.properties | Database configuration file for JPA |
| persistence.xml | Hibernate configuration file for JPA |
There's one additional entry in the application-context.xml:
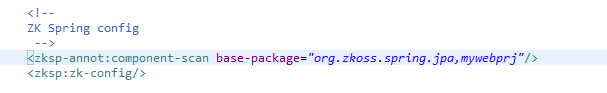
This is where the ZK Spring has been declared. In this example, ZK Spring will handled the objects that has annotation in "mywebprj" package to automatically dealt with Spring JPA , if you want to bind other packages, add entries here, for example:
<zksp-annot:component-scan base-package="org.zkoss.spring.jpa, mywebprj, mypackage1.pack1, mypackage2.pack2"/>
<zksp:zk-config/>
Then the objects with proper annotations in "mypackage1.pack1" and "mypackage2.pack2" will be handled too.
The datasource.properties store the Database connection parameters for JPA to connect database, it may be opened by a text editor to modify it's content when you need to change the datasource of this DB Form.
Library Files
Those libraries will be settled into project's /WebContent/WEB-INF/lib folder:
| hibernate-3.2.6.ga.jar hibernate-annotations-3.3.1.GA.jar hibernate-commons-annotations-3.0.0.ga.jar hibernate-entitymanager-3.3.2.GA.jar |
Hibernate library |
| org.springframework.binding-2.0.3.RELEASE.jar org.springframework.webflow-2.0.3.RELEASE.jar spring-security-core-2.0.3.jar spring.jar |
Spring framework library |
| zkspring-annot.jar zkspring.jar |
ZK Spring library |
| mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar | MySQL connector/J library |
| antlr-2.7.6.jar antlr.license.txt asm-1.5.3.jar asm.license.txt cglib-2.1_3.jar commons-dbcp-1.2.2.jar commons-pool-1.3.jar dom4j-1.6.1.jar dom4j.license.txt ejb3-persistence-1.0.1.GA.jar javassist-3.4.GA.jar geronimo-jta_1.0.1B_spec-1.1.1.jar |
Other required libraries & required license declaration |
Those libraries are provided by ZK Studio, so you don't have to download and install those libraries by yourself. (JDBC jar files are copied from local disk where you configured in DTP JDBC profile.
Customization of the Generated Application
You can customize the generated DB Form source code to meet your specification, here are two examples:
Modify the Source Code
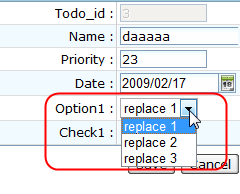
If you had configure an edit field to use a <listbox> for a column certain column in the Detail View Configuration Page of DB Form Builder, the generated result showing on the browser would like this:
And the source code of View, that is the zul file todo2.zul, is like :
<row>Option1 :
<listbox id="option1" model="@{todo2Model.option1Model}"
selectedItem="@{todo2Model.selected.option1,save-when=none}" mold="select">
<listitem self="@{each=zx6}"><listcell label="@{zx6}"/></listitem>
</listbox>
</row>
It uses a select mold <listbox> to show the drop-down on screen. And by above code segment, you can find that the content of this <listbox> is generated by the model todo2Model.option1Model, since in MVC architecture the model is manipulated by the "Controller"[2],so let's take a look at the source code of "Controller", the Todo2Controller.java:
@Controller @AppliedTo("todo2Win")
public class Todo2Controller extends mywebprj.todo2.base.Todo2ControllerBase {
@AfterCompose
public void afterCompose() {
super.afterCompose();
//TODO: MUST IMPLEMENT YOUR OWN.
List option1Model = new ArrayList();
option1Model.add("replace 1");
option1Model.add("replace 2");
option1Model.add("replace 3");
todo2Model.setOption1Model(option1Model);
}
}
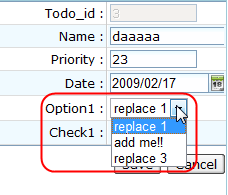
As you can see from the source code, the Todo2Controller sets an ArrayList as the list model for todo2Model.option1Model, therefore, if I change the option1Model.add("replace 2"); to option1Model.add("add me!!");
The resulting combo box content of the Option1 field editor in that DB Form will be:
The second option in combo box has been changed.
Assign Primary Key Manually
If you have select By Code/User Input in the Primary Key Creation option in ORM Configuration Page, it is up to the responsibility to create the value of primary key in the code logic in DB Form or leave it for user input, I'll show how to do that in this example.
First, I've created a DB Form by using DB Form Builder, in the ORM Configuration Page, I configure the page like this: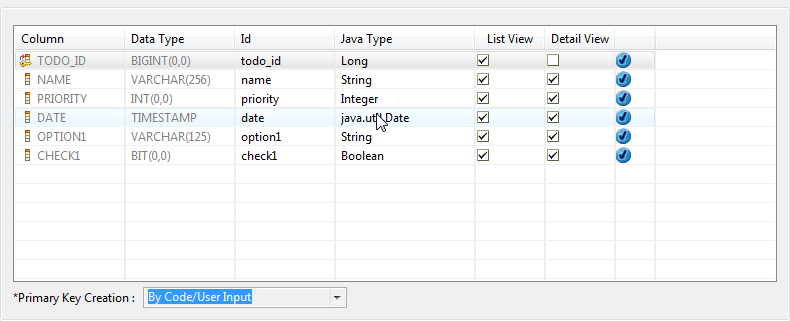
It tells DB Form Builder not to generate the editing field on the right editing panel for "todo_id", which is the Primary Key in this example, and set the Primary Key Creation to be created by code, not by auto-increment function which is provided by the majority of Databases.
Then add the following code to the "controller" java source file:
package mywebprj.todo2;
...
import java.util.Date;
...
@Scope("idspace")
@Controller @AppliedTo("todo2Win")
public class Todo2Controller extends mywebprj.todo2.base.Todo2ControllerBase {
...
@Override
protected void beforeCreate() {
Date now = new Date();
todo2Model.getSelected().setTodo_id(now.getTime());
super.beforeCreate();
}
...
}
Here I override the beforeCreate() method, this method will be called before the Hibernate doing the processing of creating new entry, as the code depicted, it will set the value of "todo_id" as the current time value of Java Date object on this line: todo2Model.getSelected().setTodo_id(now.getTime()); (Use time value as primary key isn't satisfied in a real application, in real case , the primary key value should depends on your logic and is unique in any time).
And the result is just as expected: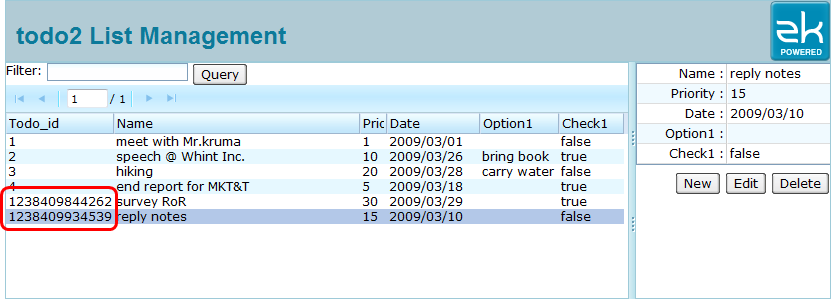
Conclusion
DB Form Builder is a powerful utility which can help you quickly and easily create a form application without spending much time in writing boilerplate code, and since it is based on the MVC architecture, it is also easy to modify the look & feel (the "view") of DB form and you can change the content of datasource (the "model") of the DB form without too much trouble.
References
- ↑ DB Form is a data operation process which is based on the MVC architecture of ZK + Spring + Datasource (ex: use JPA or Hibernate to connect Database).
- ↑ See the Solution section of Java BluePrints Model-View-Controller: http://java.sun.com/blueprints/patterns/MVC-detailed.html
| Copyright © Potix Corporation. This article is licensed under GNU Free Documentation License. |