Integrate Spring Security with ZK"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
As you can see, despite those ordinary Spring Context Listeners(''RequestContextListener'' and ''ContextLoaderListener''), we declared ''HttpSessionEventPublisher'' and ''springSecurityFilterChain'' for Spring Security. Here the ''HttpSessionEventPublisher'' is optional and it is designed for Spring Security to do detailed concurrent session control, the ''springSecurityFilterChain'' is the main hook for all Spring Security's functionality to the application, it's required and must be named '''springSecurityFilterChain'''. | As you can see, despite those ordinary Spring Context Listeners(''RequestContextListener'' and ''ContextLoaderListener''), we declared ''HttpSessionEventPublisher'' and ''springSecurityFilterChain'' for Spring Security. Here the ''HttpSessionEventPublisher'' is optional and it is designed for Spring Security to do detailed concurrent session control, the ''springSecurityFilterChain'' is the main hook for all Spring Security's functionality to the application, it's required and must be named '''springSecurityFilterChain'''. | ||
| + | ==applicationContext-security.xml== | ||
| + | Here in this project, I separated Spring's ''ApplicationContext.xml'' to two files, the original ''ApplicationContext.xml'' is for backend bean and sevice bean declarations, and the additional ''applicationContext-security.xml'' is for Spring Security's configuration only. | ||
| + | In ''applicationContext-security.xml'', there are two major elements we have to setup, the ''<http>'' element and the ''<authentication-manager>'' element. | ||
===Http Element Setting=== | ===Http Element Setting=== | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 26 February 2013
Ian Tsai, Engineer, Potix Corporation
March 04, 2013
ZK 6.5.X, Spring Security 3.1.2
Introduction
Spring Security is a common solution for developer to serve security needs in a Java web application, it is widely used and is a proven technology. However, due to its nature to protect resources by pattern matching through URL, it's not that obvious for application developer to delegate Spring Security with general amount of ajax frameworks which use Json format in form to structure meta-information.
So in this article, I'll introduce how to integrate Spring Security with ZK seamlessly by going through the construction of a simple demo application(An article publish and editing system).
Resources to Download
I use Git as my source control and has stored my code at Github, you can check out the demo project from here.
If you are more comfortable to war format, you can get the archived project here.
The project is based on Maven, if you want to try different version of ZK or Spring, please change the version number in pom.xml
Demo Application Details
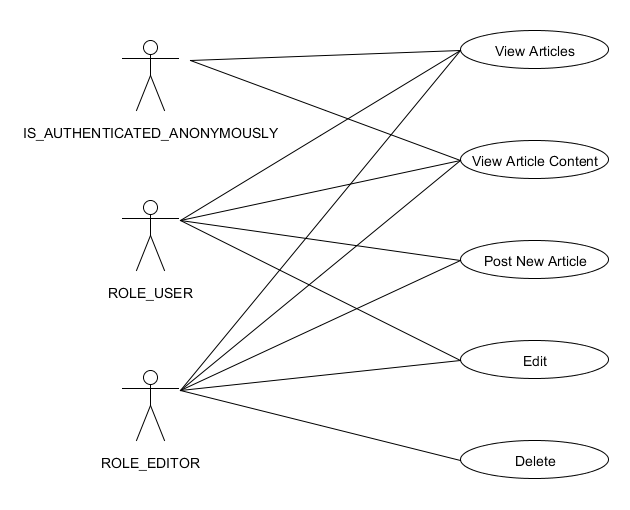
This demo application is a simple article publish and edit system which allows three kinds of user to access: user with role ROLE_USER, user with role ROLE_EDITOR and the anonymous user with default reserved role IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY.
- Anonymous user can visit the homepage which contains article list, and they can view an article's content by clicking it's link in homepage.
- User with role ROLE_USER is allowed to post new article and edit their own articles.
- User with role ROLE_EDITOR is most powerful user who is able to edit and delete any article.
This article will based on the implementation requirements of this application to demonstrate the integration of Spring Security and ZK.
Spring Security Configuration
First, let's see how to configure our project. To use Spring Security, we have to add some listener and filter declarations in web.xml:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
/WEB-INF/applicationContext-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.security.web.session.HttpSessionEventPublisher</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter><!-- the filter-name must be preserved, do not change it! -->
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
As you can see, despite those ordinary Spring Context Listeners(RequestContextListener and ContextLoaderListener), we declared HttpSessionEventPublisher and springSecurityFilterChain for Spring Security. Here the HttpSessionEventPublisher is optional and it is designed for Spring Security to do detailed concurrent session control, the springSecurityFilterChain is the main hook for all Spring Security's functionality to the application, it's required and must be named springSecurityFilterChain.
applicationContext-security.xml
Here in this project, I separated Spring's ApplicationContext.xml to two files, the original ApplicationContext.xml is for backend bean and sevice bean declarations, and the additional applicationContext-security.xml is for Spring Security's configuration only.
In applicationContext-security.xml, there are two major elements we have to setup, the <http> element and the <authentication-manager> element.
Http Element Setting
Authentication Manager Setting
Protecting a Page Request
Login Page Implementation in ZK
Securing Partial View By Using EL in ZUL
ZK's Special Component Attributes for Security
Disable & Visible
ZK EE Sever-side Event Disablement Filtering
ZK Ajax Request Security Handling
Comments
| Copyright © Potix Corporation. This article is licensed under GNU Free Documentation License. |