Shining ZATS Mimic
Hawk Chen, Engineer, Potix Corporation
April, 2012
1.0.0-RC
Opening
In agile software development, developers modify their codes frequently for requirement change or refactoring, they therefore also perform unit tests frequently to ensure the software quality. In ZK-based applications, it is hard to execute an unit test on the composer which is tightly-coupled to ZUL because it is instantiated when a ZUL is requested by a browser. The same problem arises if you want to verify a ZUL's zkbind expression with ViewModel. Hence TDD (Test-Driven Development) cannot proceed under this situation.
In some cases, agile developers may deploy their web applications to a server and test it within a browser. However, writing an automation test to control a browser is an issue, and testing for different browsers is also a trouble. Not to mention that running an unit test in an application server is time-consuming and can be an agile developer's darkest moment. But, don't be depressed, let me enlighten your path with the first light of ZK Application Test Suite (ZATS) - Mimic Library.
This project is mostly inspired by Georgi Rahnev of Telesoft Consulting GmbH, Vienna, along with a few other users and contributors. Your feedback is very valuable to us and we appreciate very much.
Comparing to previous freshly release (please refer Small Talks/2012/April/The Dawn of ZK Application Test Suite:Mimic Library), we change initialized API and support more user operations. These makes this library apply to wider testing scenario.
Mimic Library : No Server Test
Mimic library enable testers to test their composer without an application server, and of course without a browser, either. Through this library, testers can mimic user interactions to applications such as clicking or typing to verify composer's (controller layer) data and logic. All they have to do is to write a regular unit test case and use mimic library's utility class to interact components on ZUL. Then, run the test case.
No deploying to server, no rendering on browser, the unit test case can be executed in a very short period of time - this is very helpful for frequent unit testing during agile development processes.
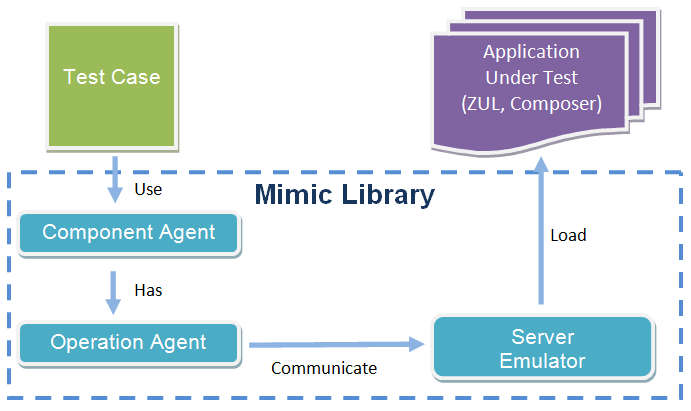
The concept is as follows:
Testers write test cases to simulate user action such as clicking or typing with operation agents. The operation agent communicates with server emulator and triggers the composer's event handlers to change the component's status. Testers can check component's properties from component agent to verify the result of user action. It might be a label changing its value or a Listbox increases by one item. These behaviors that reflect on the component's properties can be verified.
Limitation
As this library focuses on testing the composer's logic on the server side, there are some limitations you should know:
- Functions that depend on the application server cannot work.
- Test cases run in simulated environment; all functions that requires an application server does not work (e.g. JNDI, or JTA). If user's AUT (Application Under Test) project adopts such container-provided services, they need extra work to make it work normally out of a container, e.g. use Test Double like a fake object.
- Cannot test browser’s behavior.
- In ZK-based applications, some behaviors are handled by browser (JavaScript), e.g. popup menu or message dialog created at client side. As server side is not aware of these behaviors, we cannot verify it.
- Cannot test visual effects.
- It cannot verify any behaviors that doesn't reflect upon component's properties such as animations, or a component's visual effect.
Setup
Maven Project
It will be available in the near future!
Manually
Download the release zip file, add all jar under dist/lib and dist/lib/ext into your project's classpath.
Remember also add jar of your preferred unit test framework, e.g. JUnit.
Write a Test Case
The steps to write a test case are as follows:
- Setup web application content path
- Create a client to connect to a ZUL
- Query a component
- Perform an operation on a component
- Verify result by checking a component’s property
- Tear down, stop server emulator
Hello Mimic Test
To present the basic usage of mimic library, I will demonstrate how to test a simple application. This application has only one button and one label, after clicking it, the label will show "Hello Mimic".
Before diving into the source code of a test case, let me introduce some basic classes used in a test case.
- Zats
- It contains several utility methods to initialize and clean testing environment.
- Client
- It acts like a client to the server emulator and we use it to connect to a ZUL.
- DesktopAgent
- It wraps ZK Desktop object, we usually call its query() or queryAll() to retrieve ZK components with selector syntax supported in SelectorComposer
- For available selector syntax, please refer to javadoc or Small Talks/2011/January/Envisage ZK 6: An Annotation Based Composer For MVC
- ComponentAgent
- It mimics a ZK component and determines which operation you can perform on it. We can also get ZK component property's value from it.
- It also has query() , it means to find targets among its child components.
- OperationAgent (ClickAgent, TypeAgent, SelectAgent...)
- To mimic a user operation to a ZK component.
- We name it "Agent" because it's not really the user operation itself. It's an agent to mimic user operation on a component.
Hello Test Case
We write the test case with JUnit 4 annotation, please refer to JUnit 4 in 60 seconds.
HelloTest.java"
//remove import for brevity
public class HelloTest {
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
Zats.init("./src/main/webapp");
}
@AfterClass
public static void end() {
Zats.end();
}
@After
public void after() {
Zats.cleanup();
}
@Test
public void test() {
DesktopAgent desktop = Zats.newClient().connect("/hello.zul");
ComponentAgent button = desktop.query("button");
ComponentAgent label = desktop.query("label");
//button.as(ClickAgent.class).click();
button.click();
assertEquals("Hello Mimic", label.as(Label.class).getValue());
}
}
- Before starting a test, we have to call Zats.init() and pass root directory where ZUL pages are stored as a parameter. Most of the times, it is located in your web application's content root folder. In our example, we use maven default project structure.
This method initialize testing environment and starts the server emulator. (line 5)
- Of course, we start the server emulator at @BeforeClass , we should stop it by Zats.end() . (line 10)
- We should call Zats.cleanup() to clear desktop before opening another ZUL. (line 15)
- The first statement of a test case is to create a client and connect to a ZUL page, like a browser visits a ZUL. The connect() returns a DesktopAgent and we usually retrieve ComponentAgent from it to perform user operation. (line 20)
- Before we can mimic a user action to a component, we should retrieve a ComponentAgent. Empowered by selector syntax, DesktopAgent .query() is a powerful tool to retrieve it. As the ZUL contains only one button, we can query it by component name: query("button") (line 22)
- As we don't have a browser screen to view, we cannot interact with a component by mouse's pointer. To mimic a user action, we have to convert ComponentAgent to one of the operation agents. The conversion method as() will check for available operation for the target ComponentAgent . For example, you cannot type something in a Label, If you try to convert it to a non-available operation agent, you will get an exception. (line 25)
- For convenience, ComponentAgent provides shortcut methods for commonly used operations like click() . It automatically converts for you. (line 26)
- To verify test result, we also can use ComponentAgent.as() to convert it as a ZK component then get its property by getter methods. (line 27)
Operation Agent Usage
In order to mimic user operation to ZK components, our library provide various operation agents. You can find all supported under package org.zkoss.zats.mimic.operation including check, click, close, focus, key stroke, select, multiple select, type, select by index, and render . We support those commonly-used operation first and will keep adding more operations.
Click
ClickAgent helps us to mimic clicking a component in general intention. It could trigger onClick, onDoubleClick, or onRightClick event. Because most of user action is done by clicking, to avoid confusing
According to ZK Component Referenece, all components that inherit HtmlBasedComponent support click, double click, and right click.
@Test
public void test() {
DesktopAgent desktop = Zats.newClient().connect("/click.zul");
ComponentAgent label = desktop.query("#mylabel");
ComponentAgent eventName = desktop.query("#eventName");
label.click();
assertEquals("onClick", eventName.as(Label.class).getValue());
label.as(ClickAgent.class).doubleClick();
assertEquals("onDoubleClick", eventName.as(Label.class).getValue());
label.as(ClickAgent.class).rightClick();
assertEquals("onRightClick", eventName.as(Label.class).getValue());
}
Type
Select
Multiple Select
Open
Close
Summary
Download
[? Example Project].
Comments
| Copyright © Potix Corporation. This article is licensed under GNU Free Documentation License. |