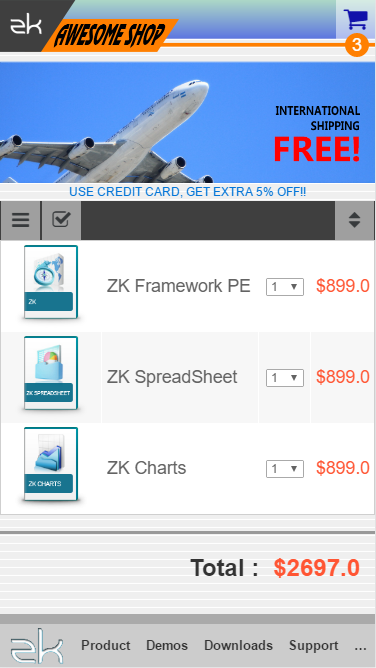
UI Pattern Bootstrap and Borderlayout
Sefi Lin, Engineer, Potix Corporation
Jun 2, 2016
ZK 8.0.2
Introduction
More and more mobile devices are appearing on the market today, meaning the ability to browse on small screens has now become a necessity. To meet this demand, ZK provides a variety of layout components to help customers build their own user interface, such as TableLayout, VLayout, HLayout or BorderLayout. However, these layouts are not designed for mobile device, which leads to the question- how can we improve our user experience on mobile devices? One of the solutions is to rely on RWD frameworks such as Bootstrap. This article will show how to build a RWD ZK page with BorderLayout and Bootstrap.
Demo
Video:
Prerequisites
- ZK 8.0.2 or later
- Bootstrap 3 knowledge, read here
Idea
This demo shows a simple shopping cart. Since we expect the page to support RWD, we would need to design two different layout templates; one is for desktop browser written in ZK BorderLayout, and the other is for mobile device browser written in Bootstrap. We suggest using the same MVVM module to synchronize data and applying the new feature in ZK 8.0.2 called "MatchMedia" to switch each templates. In this case, you will then be able to define more templates for other devices in different screen sizes.
Structure
This image explains the relationship of two templates. You can see that each template's block corresponds to another template's block. The desktop template layout on the right side uses ZK Borderlayout, while the mobile template layout on the left side follows the standard Bootstrap layout rules.
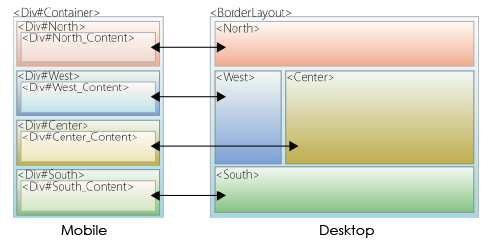
- To learn more about Bootstrap layout grid system, please read here
Main page
We use a MVVM model to control which template will be displayed. The following contains the source code of the main zul page:
<?meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"?>
<zk>
<div viewModel="@id('vm') @init('org.zkoss.zkshopcart_MVVM')" width="100%" height="100%">
<apply template="@load(vm.layoutTemplate)"/>
</div>
</zk>
The following are is MVVM java code. For now it simply displays the desktop layout. We will discuss how to detect which template will be displayed later in the section Media Queries.
public class zkshopcart_MVVM {
private String _layoutTemplate = "desktop_layout" ;
public String getLayoutTemplate() {
return _layoutTemplate;
}
}
Desktop layout template
This demo desktop layout template we use BorderLayout, without east block, we only use north, west, center and south four blocks. the north is the header, west block is a simple menu tree, center block is main block contains shopping cart items, and the final part south block is the footer.
<template name="desktop_layout">
<borderlayout>
<north>
<apply templateURI="includes/header.zul"/>
</north>
<west width="160px">
<apply templateURI="includes/menu.zul"/>
</west>
<center autoscroll="true">
<apply templateURI="includes/shoplist.zul"/>
</center>
<south>
<apply templateURI="includes/footer.zul"/>
</south>
</borderlayout>
</template>
Mobile layout template
Similar with desktop layout template, the mobile layout template has four blocks too, these blocks follow standard bootstrap rules. The typical layout for mobile is in vretical order, these blocks from top to bottom are header, menu, content and footer normaly, each Divs(North, West, Center and South) are a row, and the xxx_content inside each block is a full width column.
<template name="mobile_layout">
<div sclass="container-fluid">
<div id="north" sclass="north row">
<div id="north_content" sclass="col-xs-12 ">
<apply templateURI="includes/header.zul"/>
</div>
</div>
<div id="west" sclass="west row">
<div id="west_content" sclass="col-xs-12">
<apply templateURI="includes/menu.zul"/>
</div>
</div>
<div id="center" sclass="center row">
<div id="center-content" sclass="col-xs-12">
<apply templateURI="includes/shoplist.zul"/>
</div>
</div>
<div id="south" sclass="south row">
<div id="south-content" sclass="col-xs-12">
<apply templateURI="includes/footer.zul"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
The id is not essentially, but we adding the identity makes the code more readable. The sclass "container-fluid" at line 2 tell Bootstrap this container is a full width container, "row" at line 3, 8, 13, 18 means this block is a row, and "col-xs-12" at line 4, 9, 14, 19 means this block is a column with full width regularly.
Media Queries
We use MatchMedia Queries defined the condition when the template should be switched, in this demo, if screen width greater than 640px will show desktop template, otherwise shows mobile template. Remember to add @NotifyChange("*") after MatchMedia Queries to notify ZK update UI.
public class zkshopcart_MVVM {
private String _layoutTemplate = "desktop_layout" ;
@MatchMedia("all and (max-width : 640px)")
@NotifyChange("*")
public void getMobileTemplate(){
_layoutTemplate = "mobile_layout";
}
@MatchMedia("all and (min-width : 640px)")
@NotifyChange("*")
public void getDesktopTemplate(){
_layoutTemplate = "desktop_layout";
}
public String getLayoutTemplate() {
return _layoutTemplate;
}
}
Now your page has RWD and will auto switch template when screen width was changed.
Some other tips
Notice, if you want to use RWD feature (MatchMedia, Bootstrap) in your page, you must add a meta tag on top of the file to describe the viewport, it is essentially.
<?meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"?>
- More information of viewport meta, you can read here
If you want to use Bootstrap style component appearance, maybe you need to use some css to override zk's original style, for instance, following css code clear ZK's button appearance, and you can add another Bootstrap button class on this:
.z-button.btn{
background-image:inherit
}
.z-button.btn:hover,
.z-button.btn:focus{
background-image:inherit
}